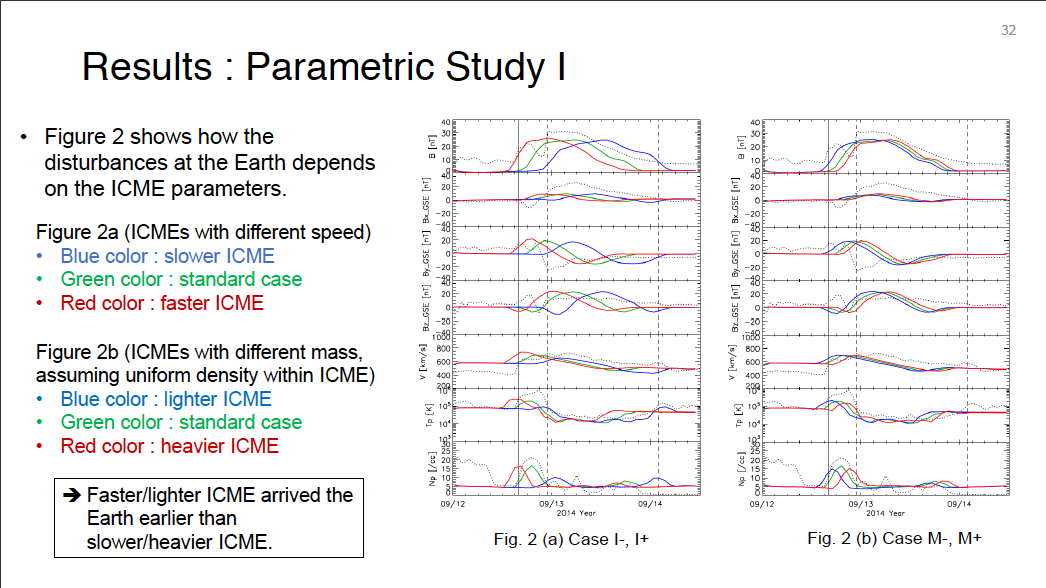
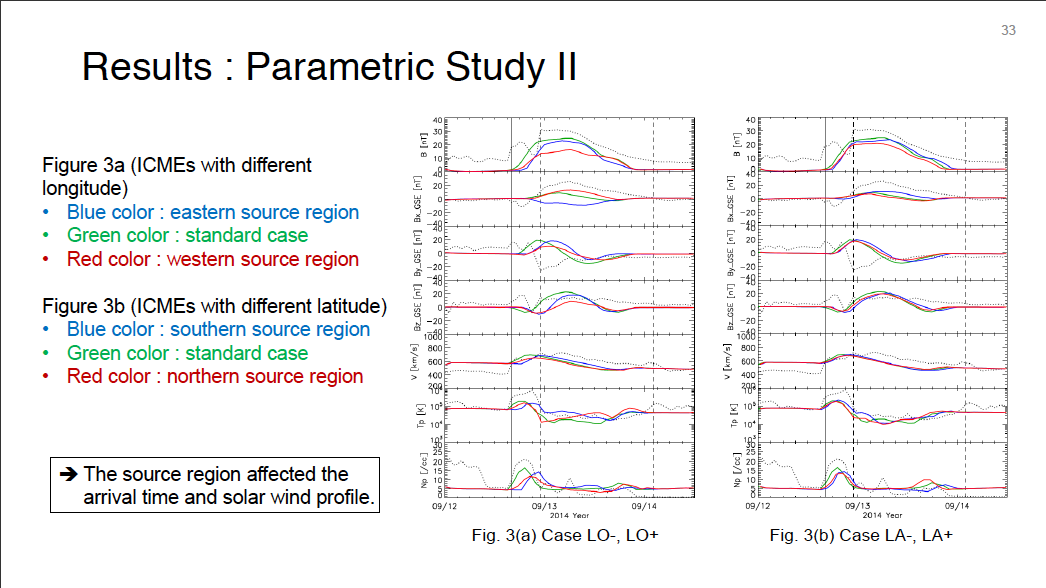
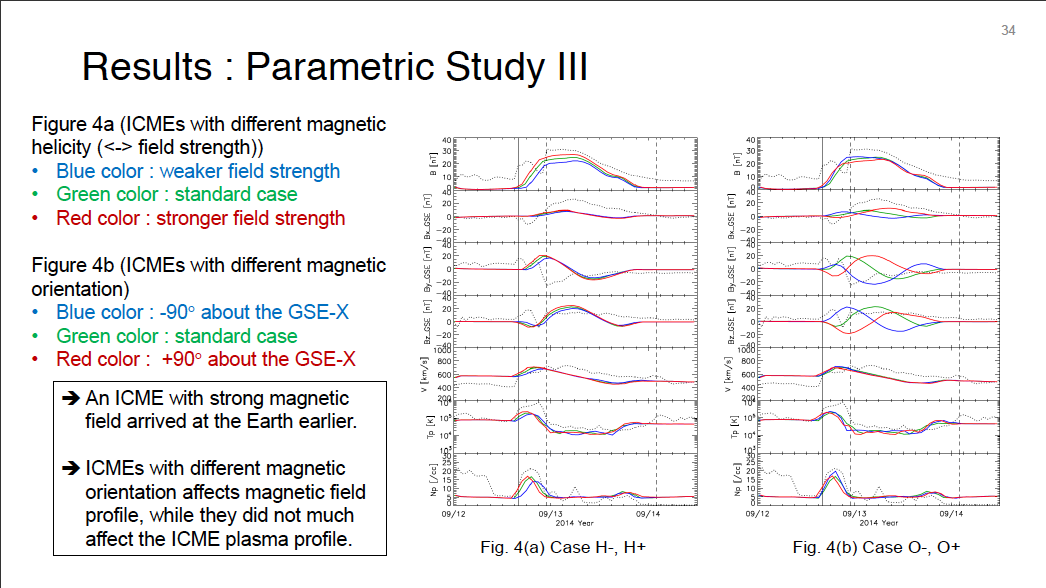
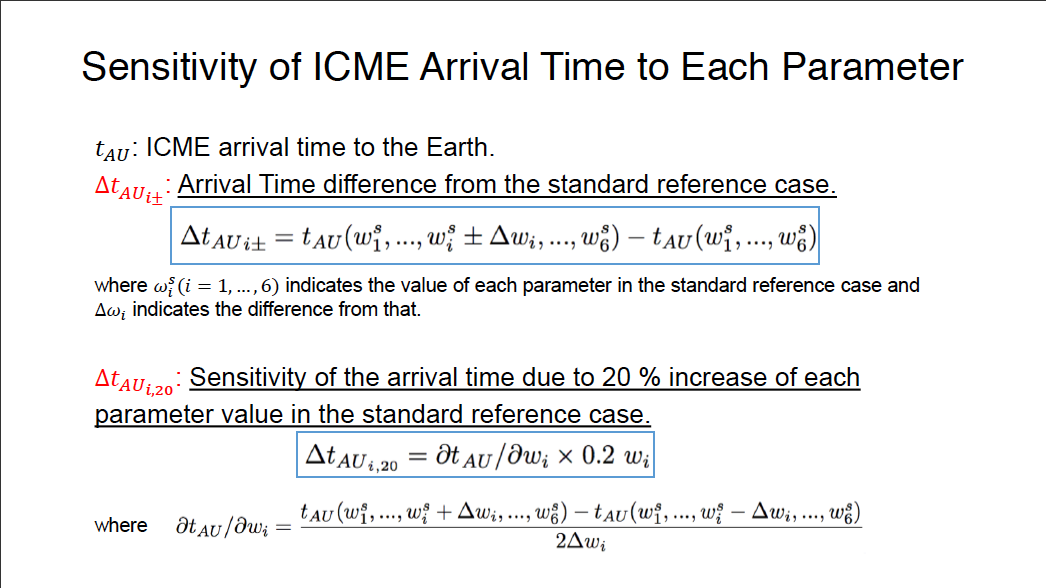
Parametric Study of ICME Properties Related to Space Weather Disturbances via a Series of Three-Dimensional MHD Simulations
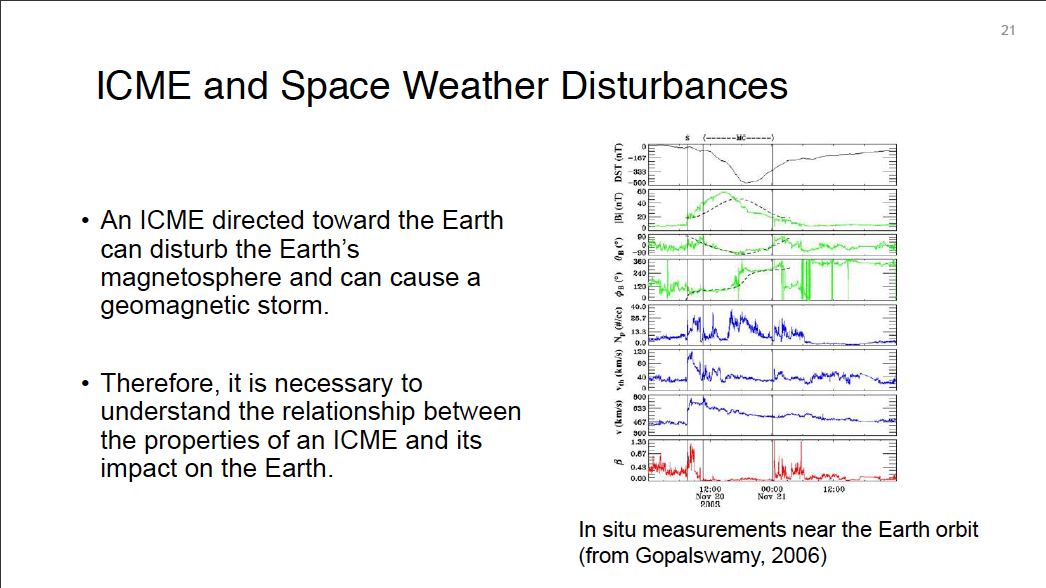
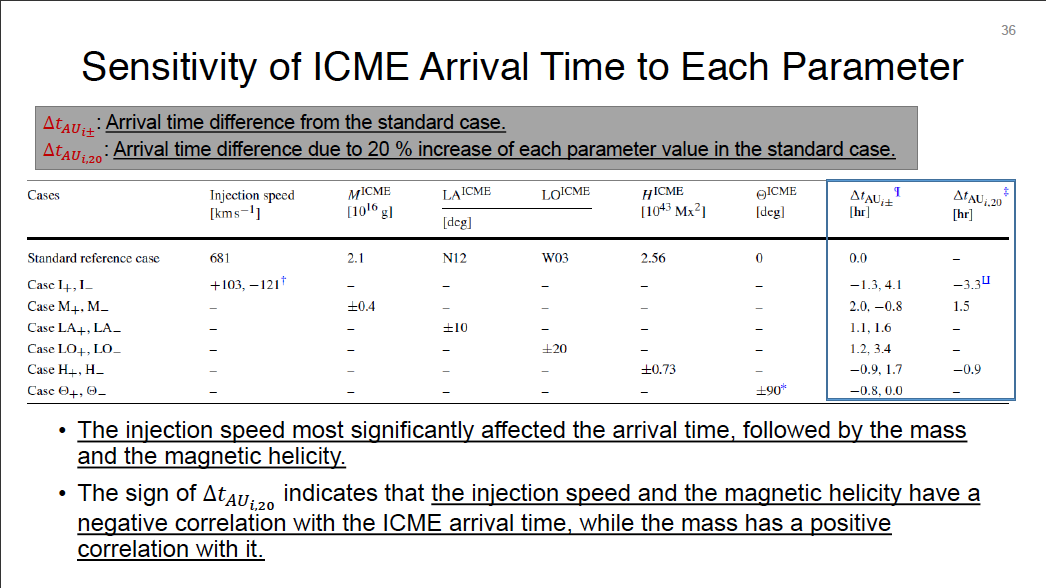
Interplanetary coronal mass ejections (ICMEs) are considered as one of the drivers of space-weather disturbances observed at an Earth orbit. We used a parameterized ICME model to investigate relations between physical properties of ICME and observed features of these disturbances. Compared to those studies focused on deriving ICME parameter values that are the best matched with observations, this study is aimed at identifying the role of each parameter in the space-weather disturbances. Toward this end, we performed a series of three-dimensional magnetohydrodynamic simulations with different sets of ICME parameter values. These parameters are location, speed, mass, magnetic field strength, and magnetic field orientation of a spheromak-type ICME, which was injected into a solar wind reconstructed from near-Sun data and interplanetary scintillation (IPS) data via an MHD-IPS tomography method. By comparing simulation results to in situ data obtained near the Earth orbit, we explained how each ICME propertiy was related to observed features of a space-weather disturbance.
Reference
An, J., Magara, T., Hayashi, K., & Y-J. Moon
Solar Physics, 294, 143